When we talk about Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)/Encryption/Digital Signature, Certificate Authority (CA) plays a key role.
In today's electronic environment when information is transferred there should be a mechanism which ensures transmission to the intended recipients and recipients should be sure of the correct origin. When you do not know the intended recipient and he/she does not know you, the following questions will arise :
how to make sure of correct delivery of the message?
How to establish trust level between such source and destination?
Answer is Certificate Authority (CA). How? See, the following diagram.
As source trusts Certificate Authority (CA) and the destination trusts the same Certificate Authority (CA). So both trust each other through common CA.
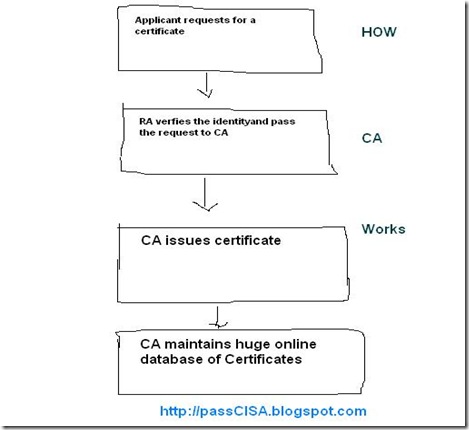
How Certificate Authority (CA) works?
Please, see the following diagram:
CA issues certificate to applicant for all verified request of Registration Authority (RA) and mantains huge database of certificates.
I believe the things are more clear to you but following Quick FAQ will clear the concept a little more.
1. What are the contents of digital certificate?
Public key
Key holder identity
Expiration date
2. What are different types of certificates?
Certificate can be of many types but important two are
Sever Certificate &
Client Certificate
3.whether all PKI will have CA?
No, but most will have.
4.When certificates can be revoked?
When keys are compromised or on expiration.
5. where expired certificate list is maitained?
in Certificate Revocation List (CRL)
6. How certificates are checked in web environment?
through web browser
This article was originally published for CISA aspirants at my CISA Made Easy Blog. This is the edited version of the same article published on Certificate Authority. I believe this article will be highly beneficial in updating the knowledge in a quick time on the subject for many Information Security Professionals.

0 comments:
Post a Comment